World Processing Tomato Council (WPTC) Forecasts 6.1% Reduction from Initial Production Intentions
Compared to 2021 production at 39.2 million mT, global production is estimated to be roughly 5% lower, finishing at 37.3 million mT. Decreases globally can be attributed to such significant factors such as water availability, land availability, and weather disturbances.
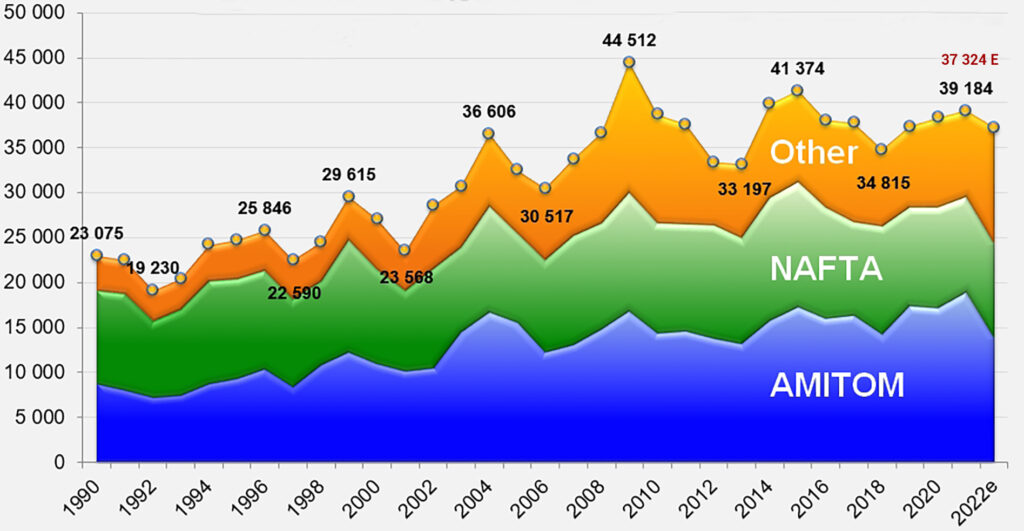
Evolution and Distribution of Global Processing 2022 | Source: Tomato News
In France, for example, the tomato growing season was the shortest in recent memory. The region processed only 142,000 tonnes, 87% of their contracted production. The southwest region experienced a good year, while heat waves affected yields in the southeast, which were down 17% at 70 tonnes/hectare.
Greece experienced heavy competition from alternative crops, resulting in 340,000 tonnes processed, a significant reduction from their original intention of 420,000 tonnes.
Still running at the end of October, production in Italy was at 5.48 million mT, a 10% reduction from 2021. With 65,180 hectares planted (37,024 in the north and 28,156 in the south), Italy was not expected to reach its record 2021 crop levels this season. Drought and high temperatures in the north caused early harvesting troubles, but late-season rains helped to improve the final overall crop production of 2.885 million mT, exceeding their initial forecast. Yields of 78 tonnes/hectare were higher than their five-year average. In the south, producers processed 2.59 million mT, a slight reduction from their 2.65 million mT projection and an overall 12% decrease from 2021.
Portugal faced heat and rain challenges, with a total of 1.33 million mT produced, a reduction from the 1.45 million mT expected. Brix levels were also impacted by September rain.
Ukraine faced significant challenges this season, with Odesa becoming their primary growing and processing region since the war has impacted the Kherson and Mykolaiv regions. Production concluded the first week of November, with a projected total of 120,000 tonnes produced, a dramatic decrease compared to their 2020 and 2021 season totals of 800,000 tonnes.
Russia processed 638,000 mT, an increase from their 600,000 mT forecast. With demand significantly exceeding supply, Russian producers are struggling to navigate production amidst global sanctions facing their country. These sanctions and their impact on businesses are expected to continue and worsen for next year’s crop.
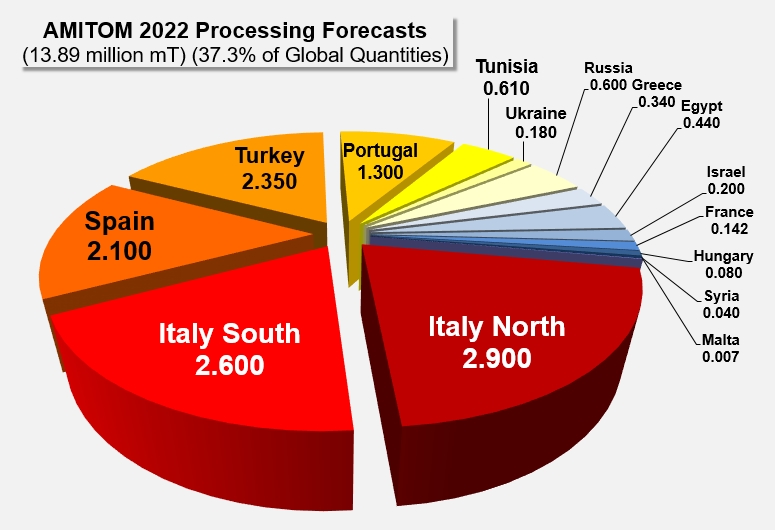
Source: Tomato News
Spain struggled with production this year, primarily due to water availability. The lack of water initially impacted their planting season, with heat in July exceeding 40°C. A few rainstorms in September caused some production facilities to pause operations. Water availability had already reduced original forecasts by 25% from 2021 levels to 2.5 million mT, but the persistent issue forced a further reduction to 33% of 2021 levels, to 2.1 million mT. Yields were down to 85 tonnes/hectare this season compared to 95 tonnes/hectare in 2021.
Turkey struggled with competing crops, notably cotton. While surface planting in the south was reduced because of the competition, other regions were able to increase their surface planting. Overall, Turkey exceeded their 2.1 million mT expectations and finished with a production of 2.35 million mT.
China originally estimated 5.8 million mT, while total processing volumes reached 6.2 million mT at the end of their processing season. With no organic production, conventional production totaled 3.68 million mT in Northern Xinjiang, 0.06 million mT in Gansu, and 1.1 million mT in Inner Mongolia. Yields were positive at 110-155 tonnes/hectare. China faces an increase in raw tomatoes, with prices now at $78/ton, 21% higher than the average of the last three years.
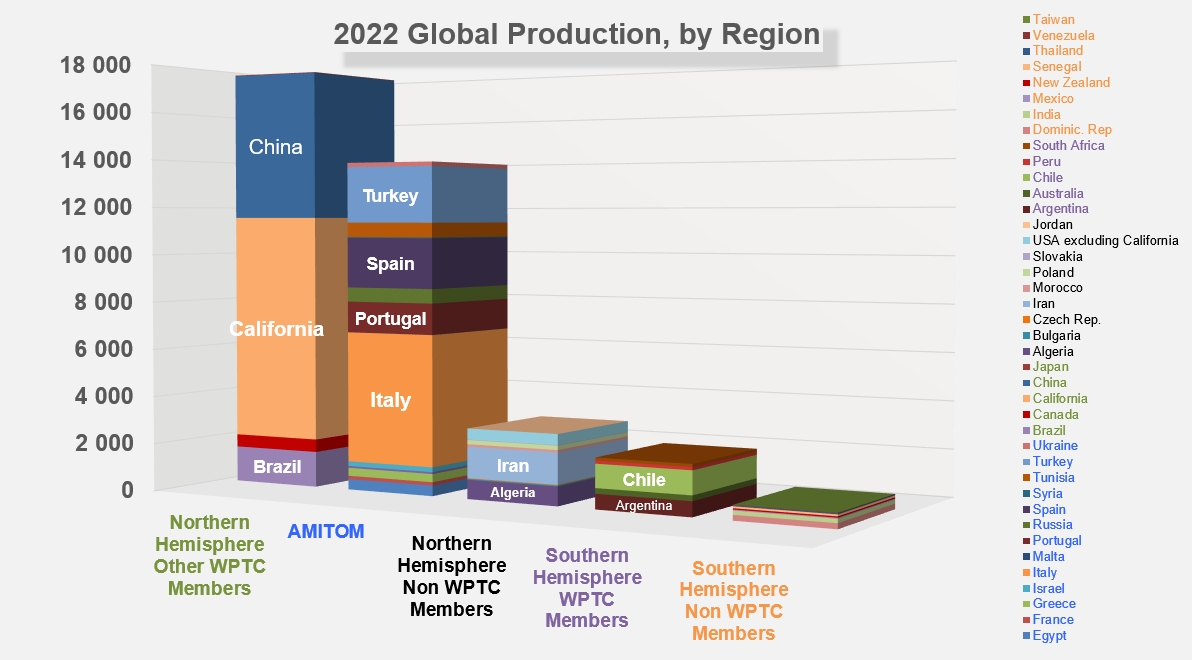
Source: Tomato News
###

Morning Star Newsletter now distributed electronically
As a reminder, Morning Star is now distributing our newsletters electronically using an email distribution vendor called Mailchimp. Your e-version will now include informative Morning Star videos and highlights. Depending on your company’s firewall, these emails may initially be directed to you spam folder.

