2022 Global Crop Intentions Increase to 39.7 million mT
As of March 15, 2022, the World Processing Tomato Council estimates the 2022 global tomato crop to increase from 39.2 to 39.7 million metric tonnes. The WPTC does note, however, that real volumes may be less than expected due to political and economic disruptions in growing regions of Ukraine and China. The WPTC met in late March and is expected to detail these forecasts further in light of the current global climate.
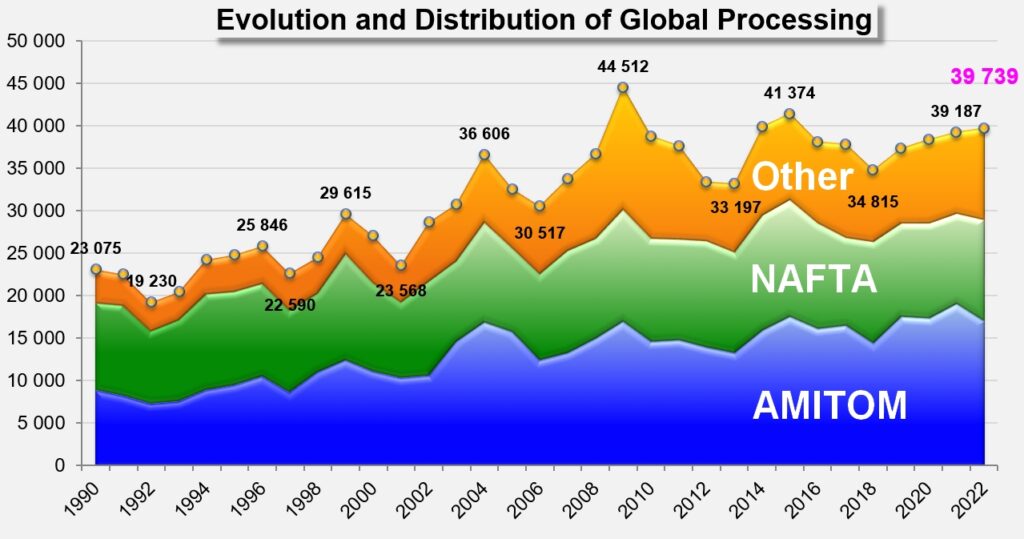
Source: Tomato News
AMITOM regions are expected to decrease their production, estimating 17.4 million mT from their regions in 2022, down from 19 million mT in 2021. Egypt has reported poor weather conditions, with colder temperatures and frost affecting color and quality. They expect to produce 440,000 tonnes. Alternative crop challenges are dominant in France, Greece, and Hungary. Greece, in particular, has seen competition from cotton and wheat crops.
Italy faces tomato price increases of more than 15% from growers, but expects the price of finished goods to increase as well. The current forecast in the North is 2.75 million mT, 10% less than 2021 and 2.65 million mT for the South, also a 10% reduction. Transportation costs continue to be an area of concern for the industry, with gas prices surging.
Despite major disruptions on the global economic front, Russia’s intentions are at 600,000 tonnes. Ukraine expects 900,000 tonnes but the likelihood of fields being able to be planted is low.
Spain faces one of the most discussed and challenging aspects of the tomato industry: lack of access to water. WPTC reports an extreme reduction in surface planting, with reductions as great as 60% and 30% in Andalusia and Extremadura, respectively. Initial estimates were at 2.2 million mT but have increased to 2.55 with a high level of uncertainty to that figure. Some growers are choosing to plant cotton, a less risky crop in Spain at the moment.
Turkey has been plagued by high inflation (90% in USD and 50% in TRL) since 2021, which challenges processors with high production costs, particularly transportation. Lack of water is another barrier to enticing farmers to grow tomatoes, many of which are choosing cotton, corn, or sugar as safer alternatives. Their surface planting intentions are expected to decrease by up to 40% less than 2021. Final crop expectations are at 1.9 million mT.
Countries outside of AMITOM also struggle with water availability, competition from crops, and increases in input costs. Brazil expects 1.8 million mT, up from 1.5 in 2021. China is predicting 5.8 million mT but, with competition from cotton, corn, sunflower, and soya beans, combined with government support for oil seeds and cereals, that number is subject to change. China also faces a labor shortage, which farm operations are increasing the use of mechanization to address.
In California, current estimates stand at 11 million mT. Processors also face increased costs for fuel and raw tomatoes in 2022, as well as competition from alternative crops.
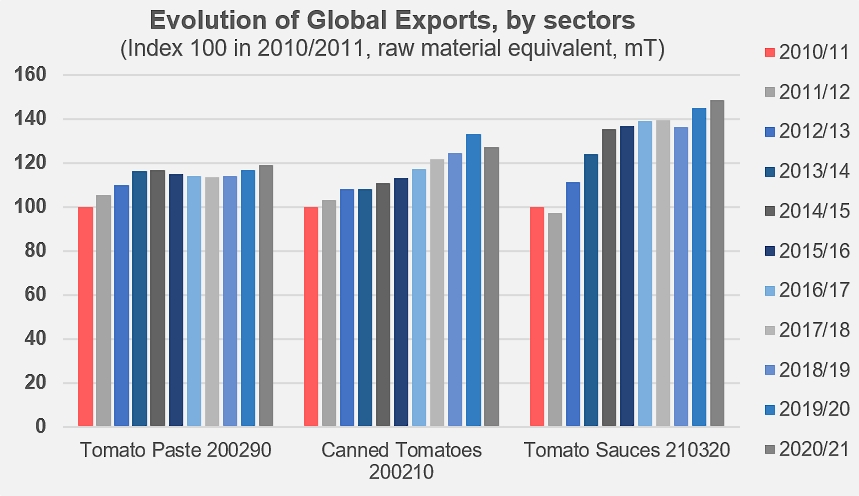
Source: Tomato News
The global marketplace in 2020 saw an increase in tomato consumption around the globe due to the pandemic. Now, in 2022, we are still seeing increases in that trend. Consumption remains at 37 million mT, which marks a 10% increase from the average three years prior in 2017 – 2019. Increases in consumption are driven mostly by the tomato sauce market, compared to tomato paste or canned tomatoes.
Regional consumption is driven by a few different areas, primarily North America, Western EU, and the middle east.
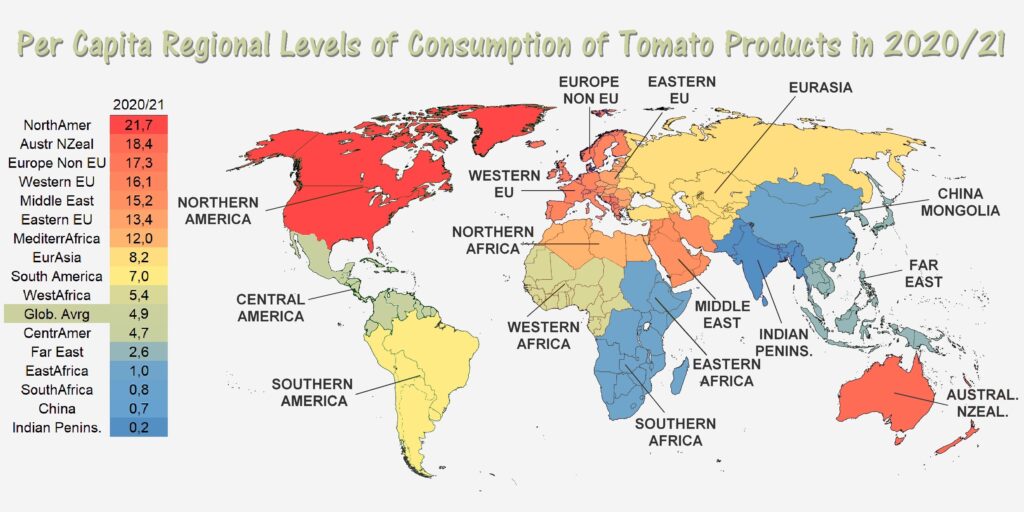
Source: Tomato News
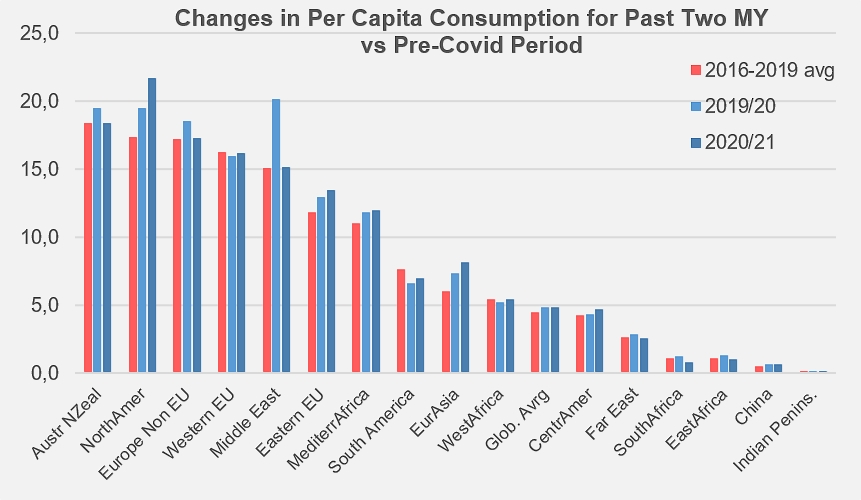
Source: Tomato News
With demand for tomato products at a historical high, there is even more pressure on growers and processors to navigate the uphill battle against water shortages, alternative crop competition, increased input costs, and other economic factors.
###

Morning Star Newsletter now distributed electronically
As a reminder, Morning Star is now distributing our newsletters electronically using an email distribution vendor called Mailchimp. Your e-version will now include informative Morning Star videos and highlights. Depending on your company's firewall, these emails may initially be directed to you spam folder.

